EMSL’s Metabolomics Workflow: A Comprehensive Approach to Analyzing Metabolites
Users can access mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance, and chemical imaging capabilities

Metabolites play a critical role in the function and advancement of biological and environmental systems, ranging from the development of bioenergy crops to the characterization of intercellular signaling.
But these small molecules are complex. Metabolites have different abundances and chemistry, making it impossible to study them using one single technique. It’s also rare to find a scientific institution that has all the instrumentation under one roof.
The Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL), a Department of Energy Office of Science user facility at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, has designed a one-stop shop to meet this need.
Using state-of-the-art, advanced mass spectrometry platforms and cross disciplinary expertise, EMSL supports user projects in targeted and untargeted metabolomics.
“Having all of them makes a huge difference,” says EMSL Chemist Nathalie Munoz.
Munoz, Chemist Chaevien Clendinen, and Mass Spectrometry Imaging Scientist Dušan Veličković recently shared how users can utilize EMSL’s metabolomics workflow for research at a free webinar at noon.
Metabolomics Instrumentation
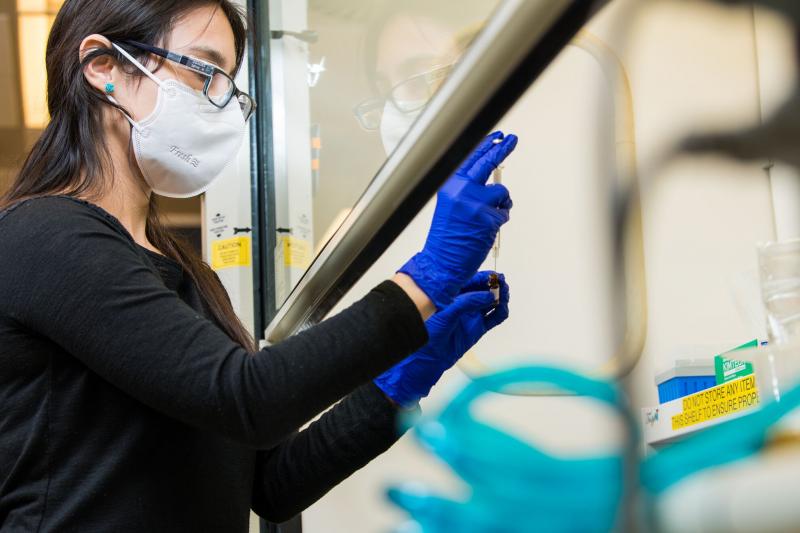

EMSL’s versatile metabolomics workflow includes mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) instrumentation and mass spectrometry imaging. These capabilities are all accessible through a single user proposal.
"We have tools that can enable us to actually analyze whatever is going on a spatial scale in environmental samples,” Veličković said. “It definitely puts our mass spectrometry at an advantage.”
The available toolkit of mass spectrometry resources includes:
-
Twenty-four instruments to comprehensively measure metabolites and lipids;
-
Four gas chromatography-mass spectrometry instruments to provide untargeted measurements of volatile and semi-volatile molecules;
-
Sixteen diverse Orbitrap instruments (including hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap and Tribrid); and
-
Four FTICR-mass spectrometry instruments.
Additionally, EMSL has four mass spectrometers dedicated to imaging. These instruments are used to investigate the spatial distribution of molecules within biological samples. This capability allows researchers to identify of hundreds of molecules in a single run, giving comprehensive information into biological and environmental process across spatial scales.
EMSL’s NMR instrumentation is also part of the metabolomics workflow, providing a powerful analytical technique that complements mass spectrometry resources. NMR is commonly used for metabolomic studies for bacteria, fungi, and plants. There are four instruments available for gathering one-dimensional and two-dimensional data for biological samples.
“The variety of potential combinations makes us unique,” says Clendinen, who is an expert in metabolomics data analysis and workflow development.
Expertise in metabolomics
EMSL’s experts in metabolomics partner with user to help their projects succeed from the proposal phase through data analysis.
For example, when a potential user submits a proposal to work with EMSL, staff like Munoz can be consulted to discuss the project in more detail and identify which analytical approaches will best suit the project. Additionally, EMSL staff work closely with researchers to make sure the experimental design will answer the questions that the collaborators have and will adapt preparation to the type of sample received, keeping continuous communication with the users to provide updates on the projects.
With EMSL’s metabolomics workflow, researchers coordinate their analysis with the instrument experts and sample prepping team to provide consistency across platforms and reduce sample prep bias. Understanding how to make sense of the data and combine it with completely different platforms is a challenge, Clendinen says. EMSL has the expertise to acquire, analyze, and interpret the different data sets, providing a comprehensive view of the biology in the systems.
“That’s what we have here,” Clendinen explains. “We have the ability to navigate that landscape with our users.”
Learn more about EMSL’s metabolomics capabilities.